1.Abstract
When you purchase an overseas Cloud Server (VPS), you will be assigned a fixed IP address. However, most beginners don't understand the difference between IPv6 and IPv4 from service providers. This article will explain in detail what IPv6 and IPv4 are and their differences.
2. What is an IP address?
IP stands for Internet Protocol address, a numerical address assigned to each network device. Its two main functions are identification and data reception and transmission. In layman's terms, it's like the address we leave when ordering takeout, but it's best not to share this address with others. IP addresses also come in several types: static IP, dynamic IP, private IP, and dynamic IP.
3. What is IPv4?
IPv4, short for Internet Protocol version 4, consists of 32 binary digits represented in decimal. It is the most widely used IP address on the internet today. In 2011, all IP addresses (approximately 4.3 billion) were issued; now, IPv4 addresses can only be reused and handled by Network Address Translation (NAT).
Address representation:
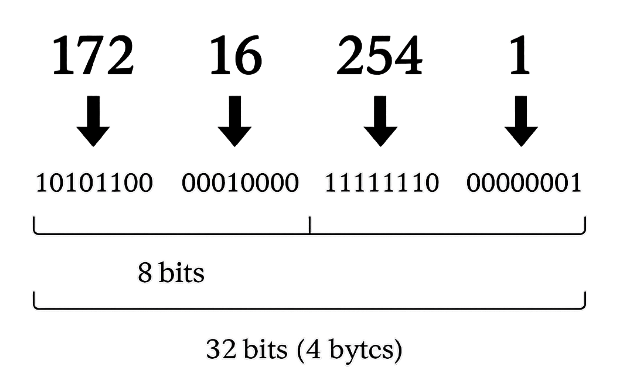
4. What is IPv6?
IPv6, short for "Internet Protocol version 6," addresses the IPv4 address exhaustion problem by using a 128-bit address space, approximately 340 trillion cubed addresses. Overall, it improves security and reduces address exhaustion.
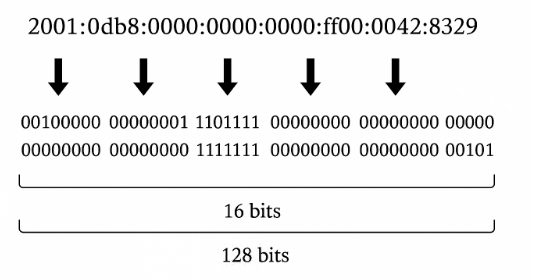
5. What are the differences between IPv4 and IPv6?
Main Difference
IPv6 does not require Network Address Translation (NAT), while IPv4 does.
Because IPv6 does not have the problem of address shortage, it does not require the use of NAT. NAT maps public IP addresses to private IP addresses to make the network more secure and save address space, so it is more suitable for IPv4.Address method
IPv4 supports multicast, broadcast, and unicast, while IPv6 is an address type that supports anycast.Data packet proportion
The minimum packet size in IPv4 is 576 bytes. In IPv6, the minimum packet size is 1208 bytes.Differences in protocols and infrastructure
The two cannot communicate with each other; an IPv6 address cannot access a website with an IPv4 address.Masthead
IPv4 uses a variable-length header while IPv6 uses a fixed-length header.
6. Why do most of them still use primary IPv4 addresses?
The reason, as I mentioned in the previous chapter, is that IPv4 and IPv6 are not interoperable. Most websites and applications we use now only support IPv4 addresses. This is because if an IPv4 user suddenly changes their IPv6 address, it's practically impossible and would lead to numerous bugs. So, what is our current situation regarding using IPv6 addresses? First:
7. Summary
Essentially, IPv6 is an enhanced version of IPv4, and it's the primary IP address for the future internet. This requires a transition period. Although most VPSs still use IPv4 addresses, IPv6 VPSs will be cheaper and more widely available. Right now, it's a matter of choosing which to use based on your network environment and connection needs; both are viable, but IPv6 is a crucial direction for the future internet.